Lack of oversight, coordination hinder efforts to reform Arizona’s rise in maternal mortality
Arizona Center for Investigative Reporting by Carmela Guaglianone, December 20, 2024: About 71 pregnant or postpartum women die in the state each year on average, with Black and Indigenous women overrepresented and rural deaths increasing.
In 2019, federal officials dedicated more than $2 million to Arizona’s Maternal Mortality Review Committee as part of a national effort to confront alarmingly high rates of maternal deaths. The funding came with a mandate: Strengthen Arizona’s process for analyzing the cases of women who die during and shortly after pregnancy, and find ways to prevent future casualties.
Since then, the committee has made a host of recommendations, from increased access to mental health care for pregnant women to expanded insurance coverage for maternal care providers, including doulas and midwives. The state has taken initial steps to implement them.
But a lack of strategic oversight and coordination, exacerbated by budget and staffing constraints, has hindered comprehensive reform, policymakers and health advocates told AZCIR. Substantive changes will require collaboration between insurance providers, health care professionals and state agencies on a scale not yet seen.
“Our question is: Where do these recommendations go, and who was responsible for implementing them?” said Cara English, a committee member and CEO of the Arizona-based Cummings Graduate Institute for Behavioral Health Studies. “Right now, it is more a situation of everyone pointing the finger at someone else, instead of collectively taking responsibility for what can be done and implemented as quickly as possible so that we can start saving lives.”
Though the Legislature was responsible for establishing the Maternal Mortality Review Committee, the group’s findings and recommendations have prompted little follow-up from lawmakers, according to state Sen. Sally Ann Gonzales, a Tucson Democrat who serves on the Senate’s Health and Human Services Committee.
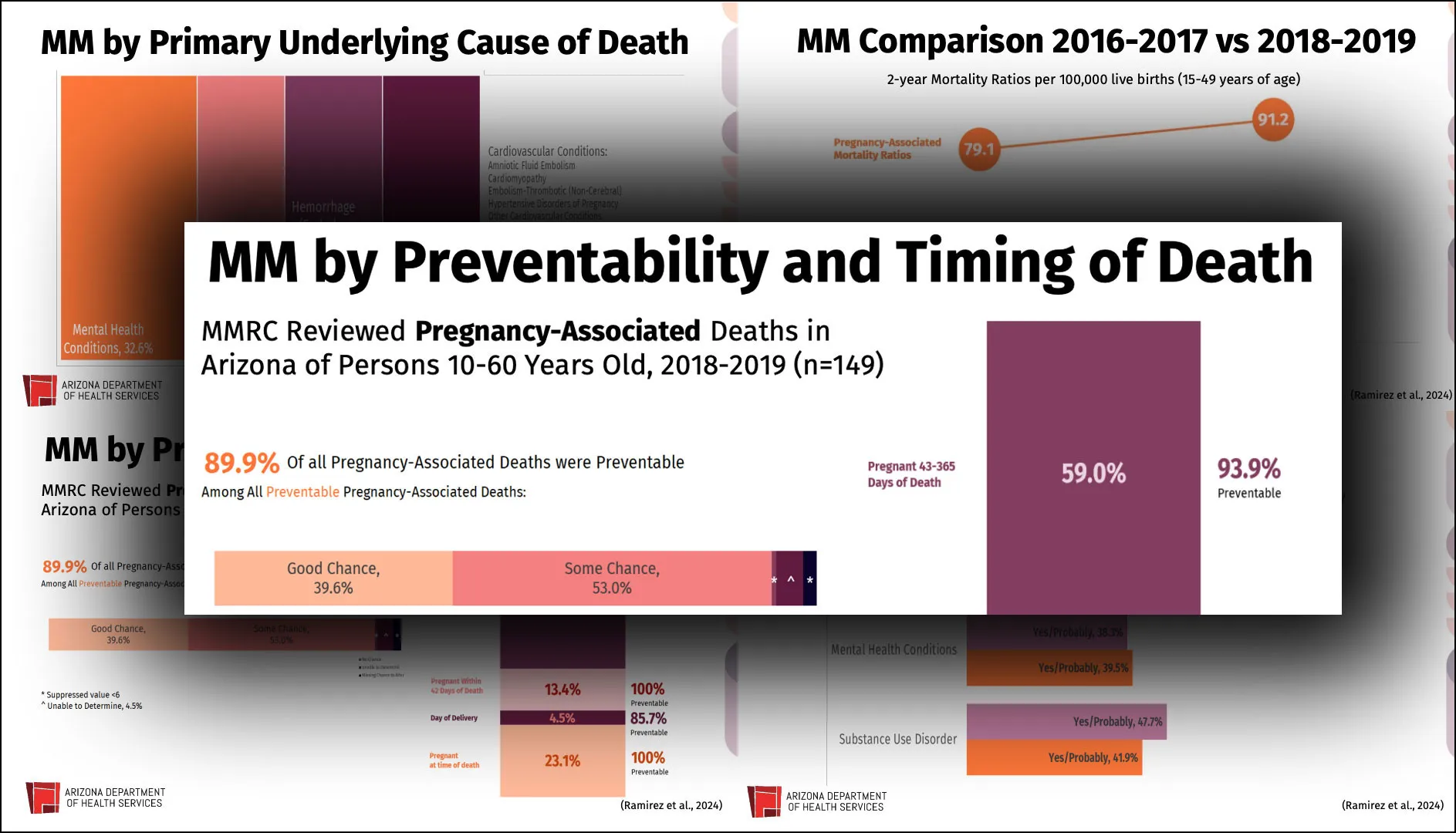
Analyses by the review committee have found that almost 90% of deaths associated with pregnancy in Arizona are preventable, and largely result from systemic issues such as a lack of access to perinatal care or social disparities, like unreliable housing or transportation. About 71 pregnant or postpartum women die in the state each year on average, with Black and Indigenous women overrepresented and rural deaths increasing.
Read more from the Arizona Center for Investigative Reporting here.




